If you’ve ever wondered how long DBT therapy is, what actually happens in a skills class, or how practices like mindfulness, meditation, and even ketamine-assisted psychotherapy fit into modern care, this guide is for you. At Oakland DBT and Mindfulness Center, we help adults and families in the East Bay and beyond build steadier emotions, stronger relationships, and a life that feels more like yours, one practical skill at a time.
What Is DBT Therapy?
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is an evidence-based approach that blends acceptance (meeting yourself where you are) with Change (learning what to do differently). In standard DBT, people typically meet weekly with a therapist and also attend a skills group that teaches concrete tools for mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. Programs were initially built as a comprehensive package, consisting of individual sessions (60 minutes weekly) and group skills training (often 2–2.5 hours weekly), alongside consultative support for the care team.
Functional Analysis (Chain Analysis) in DBT, Plain-English Version
You’ll hear DBT therapists talk about functional analysis or chain analysis. Think of it as slowing the tape: you and your therapist walk through what happened before, during, and after a problem behavior. You identify triggers, thoughts, body sensations, urges, and consequences, then design specific solutions for the links that matter most. It’s a compassionate, practical way to understand why something keeps happening and how to change it next time.

What Are the Six Main Points of DBT?
Different summaries phrase this in various ways. A helpful, plain-language way to think about “six points” looks like this:
- Acceptance & Change (the dialectic): We hold two truths at once: you’re doing the best you can, and you can learn new skills.
- Behavioral Strategies: Observe patterns, do chain analysis, practice opposite action, and focus on what you do.
- Cognitive Strategies: Notice thoughts, name judgments, and build balanced thinking.
- Skills Training: The four skills modules (mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, interpersonal effectiveness).
- Collaboration & Validation: Therapy is a partnership that honors your lived experience
- Generalization & Coaching: Practice skills between sessions and apply them in real-life situations.
Formally, standard DBT emphasizes four treatment modes (individual therapy, skills group, phone coaching, and a therapist consultation team). Still, the six ideas above describe what most people experience inside effective DBT care.
How Long Is DBT Therapy?
Short answer: It depends on your goals, history, and the format you choose. Many programs teach the full skills curriculum in about 24 weeks (roughly six months) and often repeat it to complete a year so that the tools become second nature. Individual therapy usually runs weekly alongside group. That means some people complete a 6-month round, while others opt for 12 months for more profound mastery.
At Oakland DBT and Mindfulness Center, you’ll see options ranging from DBT skills classes (modular and practical) to individual therapy tailored to your needs, so the work fits real life instead of demanding a one-size-fits-all path.
DBT Skills Classes at Oakland DBT and Mindfulness Center
Skills classes are a direct path to calmer days and steadier reactions. You learn concrete, repeatable tools you can use in the middle of stress, breathing techniques that actually help, scripts that make hard talks easier, and micro-habits that keep bad moments from becoming bad days.
Who it helps: People who feel emotions intensely, like waves; those who are tired of walking on eggshells in relationships; anyone who wants more skill and less spiraling.
Format: weekly, module-based learning with guided practice and real-world application; classes are adjuncts to individual therapy (with us or your outside therapist).
What you can expect: practical tools for stress, conflict, and communication; many participants report better coping, healthier relationship patterns, and more confidence as the weeks progress.
We offer Adult and Graduate classes (and additional tracks as available), so you can start at the right level and stay long enough to make the skills stick.

Childhood Trauma Therapy for Adults
Childhood experiences shape adult nervous systems. Trauma can show up years later as emotional reactivity, shutting down in conflict, perfectionism, or feeling oddly numb. Trauma therapy for adults helps you process memories safely, rebuild a felt sense of security, and learn in-the-moment tools for grounding and connection. DBT contributes skills for staying present, tolerating distress, and repairing relationships; your individual therapist helps weave those tools into your specific story. (At our center, individual therapy is integrative and evidence-based; more than talk, it’s practice.)
Individual Therapy for Relationship Issues
You don’t always need couples therapy to improve a relationship. Many people start with individual therapy for relationship issues, clarifying boundaries, healing people-pleasing, and learning how to communicate needs without escalating. When it makes sense, we also offer couples and family therapy to practice skills together and create shared language for Change.
Common goals we see:
- Ending the whiplash between silence and blowups
- Learning to speak clearly without apologizing for existing
- Repairing trust through small, consistent actions
- Replacing resentment with honest requests and boundaries
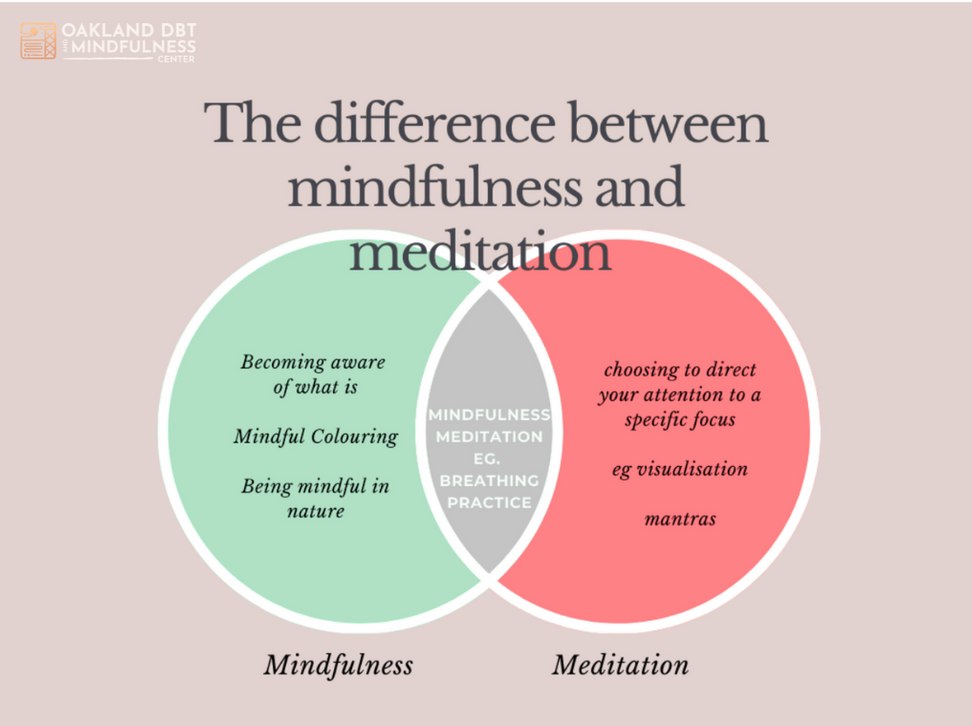
Mindfulness vs. Meditation (And Why Both Matter in DBT)
What is the difference between mindfulness and meditation?
- Mindfulness is a quality of attention, paying attention, on purpose, in the present moment, without judgment. You can be mindful while washing dishes or talking to a friend.
- Meditation is a structured practice (usually with time set aside) that trains attention and awareness. Many meditations cultivate mindfulness, but not all meditation styles are “mindfulness” per se.
What are the different types of meditation?
There’s no single official list, but common categories include focused attention (such as breathing or mantra), open monitoring (observing thoughts/sensations), and affect-centered practices (such as loving-kindness/compassion). You’ll also see movement (walking, yoga, tai chi), visualization, and others. What matters most is: does it help you regulate attention and emotion in daily life?
DBT uses mindfulness not as a lifestyle aesthetic but as a workbench: short, repeatable practices you can deploy during a tough day.
About Ketamine-Assisted Psychotherapy (KAP), and the Couples Question
What is ketamine therapy for couples?
Some clinics now offer couples protocols where one or both partners receive ketamine in a monitored setting, paired with therapeutic support focused on communication and empathic connection. Early reports and conceptual papers suggest potential benefits, but the field is still developing, and evidence is evolving.
Important safety context: Ketamine is FDA-approved as an anesthetic; it is not FDA-approved for psychiatric disorders (esketamine/Spravato is approved for treatment-resistant depression, including as a standalone option, and is administered under supervision). If you’re considering any ketamine-related treatment, informed consent and medical oversight are essential.
What the Oakland DBT and Mindfulness Center provides:
- Ketamine-Assisted Psychotherapy (KAP) is delivered with therapeutic preparation and integration, and conducted in-person for safety; we also offer psychedelic integration therapy for people processing experiences from other settings.
- If relationship patterns are a focus, we can pair KAP-related insights with individual or couples therapy to translate breakthroughs into everyday habits of connection. (Couples and family therapy are part of our services; KAP itself is medically supervised and in person.)
Local, Accessible Care, Oakland, East Bay, and Telehealth
We’re based on Piedmont Avenue in Oakland, serving the East Bay community with in-person sessions. Most services are also available by telehealth (with KAP as the exception because it requires in-person medical monitoring). Some clinicians are licensed to work virtually with clients in additional states (e.g., California, Colorado, Florida); availability can vary by therapist, so ask when you reach out.
How to get started: The fastest way to reach us is through the contact form or by phone: (510) 239.5698. Please let us know your age and whether you’re seeking an individual therapist, a DBT skills class, or couples/family support, and we’ll match you with the right option.
Putting It All Together
Therapy should feel doable. Whether you’re tackling big emotions, healing childhood trauma as an adult, or wanting fewer fights and more connection, the right mix of DBT skills + individualized therapy can make life less reactive and more intentional. Add supportive practices, mindfulness, meditation, and healthy boundaries, and you’re building something sustainable. If your clinician recommends it and it fits your clinical picture, ketamine-assisted psychotherapy may offer a catalyst for change and integration work to make insights stick.
If you’re ready to move from “I don’t know what to do in the moment” to “I have a plan, and it works most days,” we’re here to help.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How long is DBT therapy?
Many programs teach the full skills curriculum in 24 weeks (6 months) and often repeat for 1 year to consolidate skills. Individual therapy typically runs weekly alongside group. Your length will vary based on goals and clinical needs.
What is functional analysis in DBT?
It’s a chain analysis, stepping through triggers, thoughts, sensations, urges, and consequences to see why a behavior “worked” and where a new skill can change the outcome next time.
What are the six main points of DBT?
A helpful summary is: acceptance/change, behavioral strategies, cognitive strategies, skills training, collaboration/validation, and generalization/skills coaching, mapped onto DBT’s standard modes of care.
What’s the difference between mindfulness and meditation?
Mindfulness is a way of paying attention in daily life; meditation is a structured practice that trains attention (mindfulness meditation is one common type).
What are the different types of meditation?
Focused attention, open monitoring, loving-kindness/compassion, mantra, movement (walking, yoga, tai chi), visualization, and more.












